Introduction
Dogs have long been called “man’s best friend,” celebrated for their loyalty, playfulness, and companionship. But when it comes to love, many pet owners wonder: can dogs really love their humans the way we love them? While dogs may not experience emotions exactly like humans, scientific research and behavioral observations reveal that they are capable of forming deep, meaningful bonds with their owners.
Understanding canine love is not just an academic curiosity—it helps strengthen the bond between you and your dog, improve training outcomes, and enrich your everyday interactions. From tail wags and cuddles to protective behaviors and emotional support, dogs display affection in ways that are sometimes subtle and sometimes unmistakably profound.
In this post, we will explore what science says about dog emotions, the behavioral signs that indicate love, the factors influencing canine affection, and how owners can nurture this special connection. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of the ways dogs express love—and why that bond is truly meaningful.
Understanding Canine Emotions
To answer the question, “Can dogs really love their owners?” it’s essential to first understand how dogs experience and express emotions. While dogs may not feel love exactly as humans do, they are capable of attachment, affection, and complex emotional responses.

1. What Science Says About Dog Emotions
Dogs have brain structures similar to humans, particularly in areas related to emotion and reward. Studies show that dogs can experience joy, fear, empathy, and affection. When interacting with their owners, dogs often release oxytocin, the so-called “love hormone,” which strengthens bonding and attachment—just as it does in humans.
2. Signs of Attachment and Affection
Dogs demonstrate their feelings through consistent behaviors: seeking proximity, following their owners, leaning on them, or nudging for attention. These actions indicate trust, comfort, and a desire for social connection—key ingredients of canine love.
3. Differences Between Human and Canine Love
While humans often view love in romantic or abstract terms, dogs express love primarily through behavior and physical interaction. Affection in dogs is practical and relational: they show attachment through loyalty, protection, companionship, and responsiveness to your emotions. Understanding this distinction helps owners appreciate canine love on its own terms rather than expecting human-like expressions.
By recognizing and respecting how dogs express emotions, owners can better interpret signs of affection and strengthen the bond with their furry companions.
Behavioral Signs That Dogs Love Their Owners
Dogs may not use words, but their actions often speak louder than speech. Recognizing the behavioral signs of affection can help you understand how your dog expresses love and attachment.
1. Seeking Physical Contact
Cuddling, leaning against you, or licking your hands and face are common ways dogs show affection. Physical closeness demonstrates trust and comfort, signaling that your dog feels safe with you.
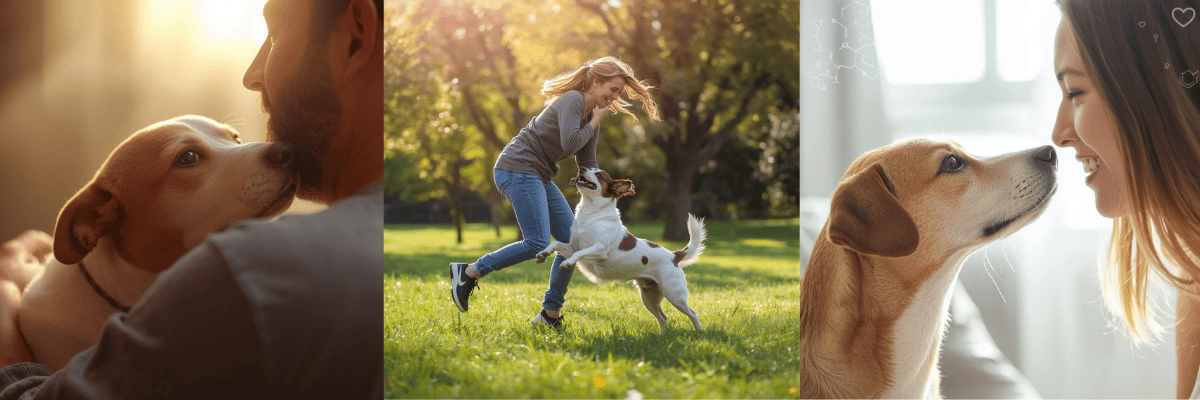
2. Excitement Upon Seeing You
Tail wagging, jumping, spinning, or vocalizing when you return home are clear indicators that your dog missed and values your presence. This enthusiasm reflects emotional attachment and joy.
3. Protectiveness and Loyalty
Dogs often exhibit protective behaviors toward their owners, such as alertness to strangers, guarding the home, or staying close in unfamiliar situations. This loyalty and vigilance is a sign of their strong bond and commitment.
4. Following You Around
If your dog prefers to stay near you, follows you from room to room, or chooses your company over others, it demonstrates attachment and a desire for connection.
5. Comfort-Seeking and Emotional Support
Many dogs sense their owner’s mood and respond accordingly. A dog may nuzzle, rest their head on you, or stay close when you’re sad or stressed. This behavior shows empathy and affection, reflecting an emotional bond similar to love.
By paying attention to these behaviors, owners can recognize genuine affection in their dogs and better respond to their emotional needs, strengthening the human-canine connection.
Scientific Studies Supporting Canine Affection
While behavioral observations suggest dogs are capable of affection, scientific research provides stronger evidence that dogs can form deep emotional bonds with their owners.
1. Oxytocin Studies
Oxytocin, often called the “love hormone,” is released in both dogs and humans during positive interactions. Studies have shown that when dogs make eye contact with their owners, both experience increased oxytocin levels, which reinforces bonding, trust, and mutual affection.
2. MRI Studies on Dog Brains
Brain imaging research has revealed that dogs’ reward centers activate when they see their owners. This response is similar to how humans react to loved ones, suggesting that dogs associate their owners with pleasure and positive emotions.
3. Behavioral Experiments
Experiments have demonstrated that dogs consistently choose familiar humans over strangers, even when offered treats from unfamiliar people. This shows that dogs value their human companions beyond immediate rewards, indicating loyalty and emotional attachment.
These scientific findings support the idea that dogs don’t just tolerate their owners—they can form meaningful, affectionate bonds that resemble love in its behavioral and emotional dimensions.
Factors That Influence a Dog’s Affection
While most dogs are capable of forming deep attachments, several factors can influence how strongly and openly they express love toward their owners. Understanding these factors can help owners nurture a stronger bond.
1. Breed Tendencies and Social Predispositions
Some breeds are naturally more affectionate, social, and people-oriented. For example, Golden Retrievers, Labradors, and Cavalier King Charles Spaniels often display more visible attachment behaviors, while other breeds may be more independent but still capable of deep bonds.
2. Early Socialization and Training
Dogs that are well-socialized from a young age tend to be more confident, trusting, and open to forming strong emotional connections with humans. Gentle, positive training reinforces love and trust.
3. Quality of Human Interaction
The consistency, attention, and kindness that owners provide play a major role in shaping a dog’s affection. Dogs thrive when their humans are responsive, nurturing, and engaged.
4. Health and Age Considerations
Puppies and young dogs may show exuberant affection, while older dogs may display more subtle signs. Health issues, pain, or stress can temporarily affect a dog’s ability to express love.
By paying attention to these factors, owners can create an environment that encourages trust, emotional security, and deep affection, helping their dog express love more freely.
How Owners Can Foster Love and Trust
Building a strong, loving bond with your dog requires consistent care, attention, and understanding. Here are practical ways to nurture affection and trust:

1. Positive Reinforcement and Affection
Reward your dog with praise, treats, or play for good behavior. Positive reinforcement strengthens trust and encourages your dog to associate you with safety and happiness.
2. Consistent Routines and Shared Activities
Dogs thrive on predictability. Regular walks, feeding times, play sessions, and training routines create a sense of security and demonstrate reliability and care, deepening emotional bonds.
3. Respecting Boundaries and Signals
Learn to recognize your dog’s body language. Respecting their need for space or rest builds trust and prevents stress, allowing your dog to feel safe expressing affection.
4. Mental Stimulation and Exercise
Engage your dog in activities that challenge their mind and body, such as puzzle toys, scent games, or interactive training. A mentally and physically fulfilled dog is more likely to be affectionate and emotionally connected.
5. Providing Consistent Care
Regular grooming, health check-ups, and attention to well-being show your dog that you care for them holistically, reinforcing the emotional bond and encouraging love.
By integrating these practices into daily life, owners can create a nurturing environment that fosters loyalty, affection, and a deep, enduring love from their dog.
Misconceptions About Dogs and Love
While dogs are clearly capable of affection, it’s important to understand how their love differs from human love and avoid common misconceptions.
1. Dogs Are Not Capable of Human-Style Romantic Love
Dogs may show attachment, loyalty, and affection, but they do not experience romantic or complex human emotions. Their love is based on social bonds, trust, and positive associations with their owners.
2. Affection Should Not Be Confused with Dependency or Fear
A dog that clings excessively or follows you constantly may be anxious or fearful rather than expressing genuine affection. True love is accompanied by comfort, joy, and trust, not just dependency.
3. Understanding Attachment vs. Manipulative Behavior
Dogs may use behaviors like whining or pawing to get attention, but this is often a learned communication strategy rather than an emotional reflection of love. Observing consistent affectionate behaviors helps distinguish genuine attachment.
By understanding these nuances, owners can interpret their dog’s emotions accurately, respond appropriately, and strengthen the bond without misreading behavior.
Conclusion
Dogs are often celebrated for their loyalty, playfulness, and companionship, and research confirms that they are capable of forming deep, meaningful bonds with their owners. While canine love may not mirror human romantic love, it is expressed through trust, attachment, physical affection, and emotional responsiveness.
By recognizing behavioral signs like cuddling, excitement upon your return, protective instincts, and comfort-seeking, owners can see the evidence of their dog’s love in everyday interactions. Science further supports this bond, from oxytocin releases to brain activity patterns that highlight dogs’ attachment to humans.
The strength of a dog’s affection depends on factors like breed tendencies, early socialization, quality of care, and health. Owners can foster love and trust through positive reinforcement, consistent routines, respect for boundaries, and mental and physical engagement. Understanding common misconceptions ensures that interactions are meaningful, nurturing, and appropriate.
Ultimately, the love dogs feel is real, profound, and rewarding. By caring for your dog thoughtfully and attentively, you create an environment where that bond can flourish, offering both emotional fulfillment and companionship that lasts a lifetime.


Leave a Reply